Vogelbusch Glucose Technology
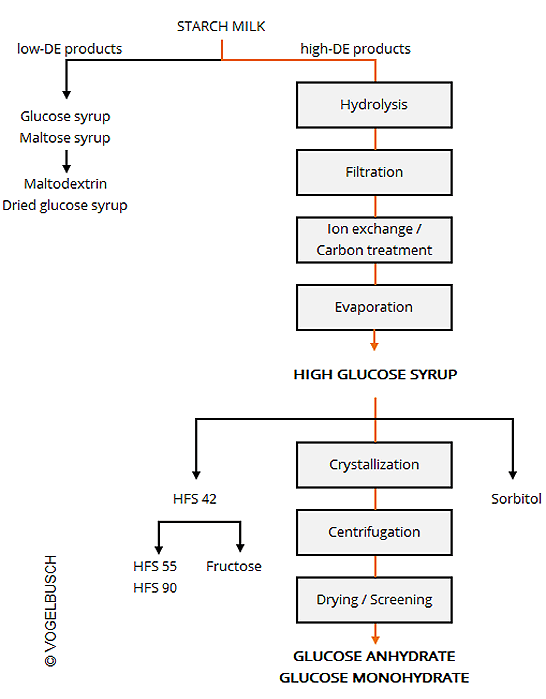
Glucose, also known as dextrose, is a natural sweetener, which is obtained from starch containing plants such as corn, wheat, rice and cassava.
As a liquid intermediate product, glucose syrup serves as a feedstock for » fermentation processes and it can be further processed to gain sorbitol or fructose. Crystallization of glucose syrup produces dextrose anhydrate or monohydrate, which are used in foodstuff as a sweetening agent, and in medical applications.
Starting out from starch milk, we design and supply plants for the production of liquid and crystalline types of glucose.